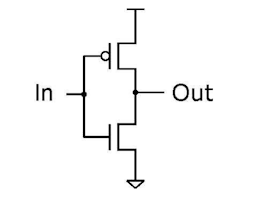
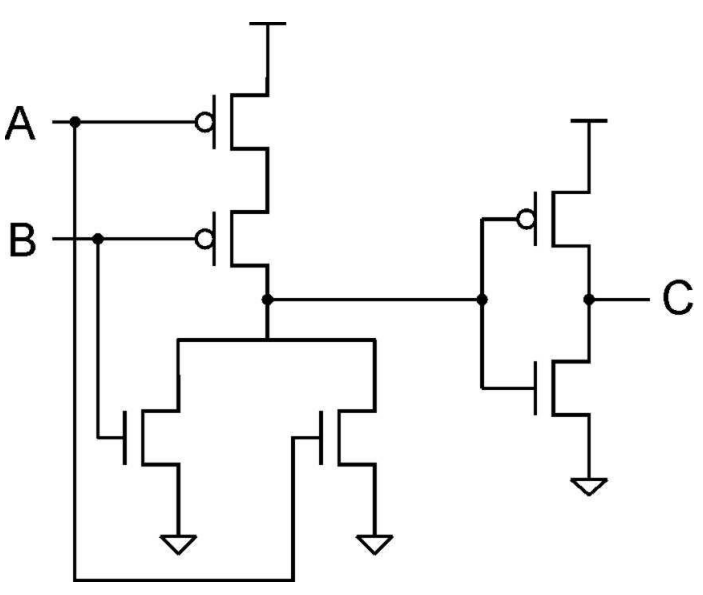
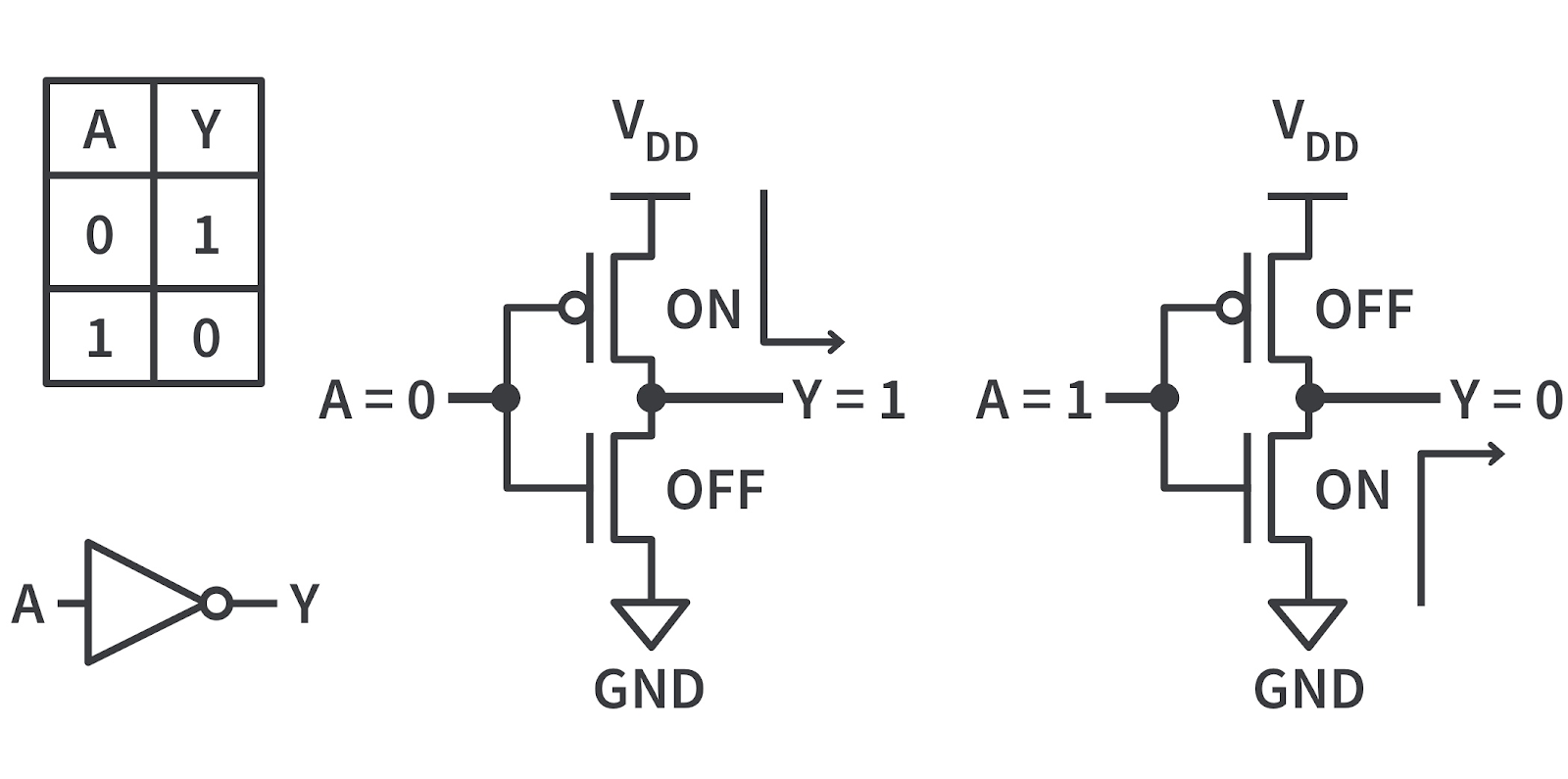
MOSFET - Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor.
MOSFET is a type of transistor used in electronic circuits for switching and amplification. It consist of metal gate electrode separated from the semiconductor channel by a thin layer of oxide, when voltage is appiled to the gate an electric field is created which controls the flow of current through the channel between the source and drain.
Source is connected to ground.
Drain is connected to load.
Gate is connected to input.
There are two main types of MOSFETs:
N-channel MOSFET (NMOS): In an NMOS transistor, the semiconductor channel is made of n-type material (electron-rich). The gate voltage controls the flow of electrons from the source to the drain. When a positive voltage is applied to the gate with respect to the source, it creates an electric field that attracts electrons, forming a conductive channel between the source and drain, allowing current to flow.
P-channel MOSFET (PMOS): In a PMOS transistor, the semiconductor channel is made of p-type material (hole-rich). The gate voltage controls the flow of holes from the source to the drain. When a negative voltage is applied to the gate with respect to the source, it creates an electric field that attracts holes, forming a conductive channel between the source and drain, allowing current to flow.










.png)

